📑Literature Review
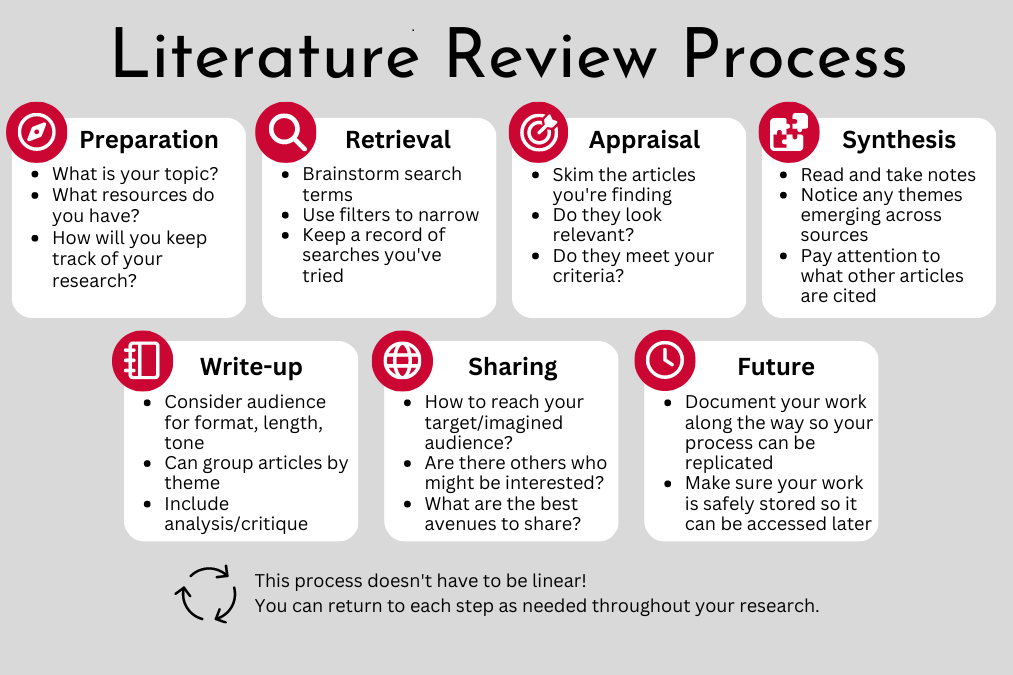
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive summary and analysis of existing scholarly literature on a specific topic or research question. It is an essential component of academic research and serves several important purposes:
Understanding the Current State of Knowledge: A literature review helps researchers gain a deep understanding of what has already been studied and published in their area of interest. It provides an overview of the key concepts, theories, and findings related to the topic.
Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By reviewing existing literature, researchers can identify gaps, contradictions, or areas where further research is needed. This helps them refine their research questions and objectives.
Contextualizing Research: A literature review places the researcher's work within the context of previous studies. It shows how their research contributes to the broader academic conversation and builds upon prior work.
Selecting Methodologies and Approaches: Researchers can learn from the methods and approaches used in previous studies. They can identify which research methods have been successful in addressing similar questions and which might be suitable for their own research.
Supporting or Challenging Hypotheses: Existing literature can provide evidence to support or challenge the hypotheses or claims made in a research study. Researchers can use this information to refine their own arguments and theories.
Citing Relevant Sources: A literature review ensures that researchers appropriately cite and reference the relevant sources in their field. It demonstrates that they are aware of and respect the contributions of other scholars.
A literature review typically involves searching for and reviewing academic articles, books, conference papers, and other scholarly sources related to the chosen topic. Researchers then summarize and synthesize the key findings, theories, and methodologies from these sources in their review.
The structure and depth of a literature review can vary depending on the purpose and requirements of the research project. It can be a standalone document or a section within a larger research paper or thesis. Regardless of its format, a well-conducted literature review is an integral part of the research process, helping to build a solid foundation for new research and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in a particular field.
Similarities Between SLR and Literature Review
A systematic literature review (SLR) is a specialized type of literature review, so they share several similarities with traditional literature reviews. However, there are also key differences. Here, I'll outline the similarities between the two:
Both Involve Reviewing Existing Literature: Both traditional literature reviews and systematic literature reviews involve the process of searching, selecting, reviewing, and synthesizing existing scholarly literature on a specific topic or research question.
Aims to Summarize and Analyze: The primary goal of both types of reviews is to summarize and analyze the existing body of knowledge on a given subject. They aim to provide a comprehensive overview of relevant studies, theories, findings, and methodologies.
Identify Gaps in Knowledge: Both types of reviews help researchers identify gaps or areas where further research is needed. By assessing the existing literature, researchers can determine what has already been studied and where new research contributions can be made.
Contribute to Research Context: Both types of reviews help contextualize research within the broader academic conversation. They demonstrate how a particular study fits into the existing body of knowledge and builds upon prior work.
Citation and Referencing: Both types of reviews require researchers to appropriately cite and reference the sources they consult. This ensures that prior research is acknowledged and credited.
Critical Analysis: In both cases, critical analysis is essential. Researchers should evaluate the quality of the sources they review, including the methodology used in the studies, the validity of the findings, and the relevance to their research question.
Despite these similarities, there are significant differences between traditional literature reviews and systematic literature reviews:
Methodological Rigor: Systematic literature reviews adhere to a rigorous and predefined methodology. They have a structured and systematic approach to searching for, selecting, and evaluating sources, which minimizes bias and enhances the reliability of the review. Traditional literature reviews may be less systematic and structured.
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria: Systematic literature reviews often establish strict inclusion and exclusion criteria to select studies, aiming for a more objective and standardized approach. Traditional literature reviews may have more flexibility in source selection.
Explicit Search Strategy: Systematic reviews have an explicit and well-documented search strategy that outlines the databases, keywords, and search terms used to identify relevant studies. Traditional reviews may not provide as much detail about their search methods.
Quantitative Analysis: Systematic reviews often include a quantitative analysis, such as meta-analysis, to statistically synthesize the findings of multiple studies. Traditional reviews may rely more on qualitative synthesis.
In summary, while both traditional literature reviews and systematic literature reviews share the goal of reviewing and analyzing existing literature, systematic reviews are characterized by a more rigorous and structured methodology, while traditional reviews may be less formal and systematic in their approach. The choice between the two depends on the research objectives and the level of rigor required for the study.
Last updated